# How to Calculate Dew Point
## Understanding Dew Point
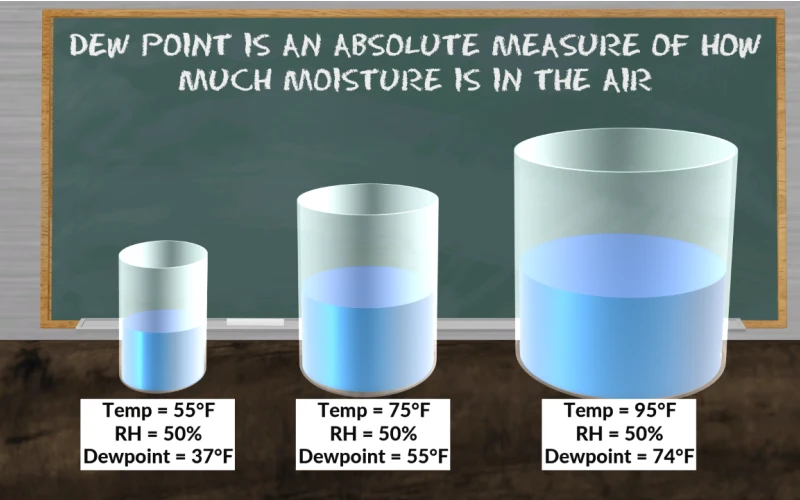
Dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to the formation of dew, fog, or clouds. It’s a crucial measurement in meteorology, HVAC systems, and various industrial processes. Knowing how to calculate dew point helps predict condensation and assess comfort levels in different environments.
## The Basic Formula
The most commonly used formula for calculating dew point is the Magnus formula:
Td = (b × α(T,RH)) / (a – α(T,RH))
Where:
– Td is the dew point temperature
– T is the air temperature in °C
– RH is the relative humidity (as a decimal, e.g., 50% = 0.5)
– a and b are Magnus coefficients (a = 17.27, b = 237.7°C)
– α(T,RH) = (a × T)/(b + T) + ln(RH)
## Step-by-Step Calculation
Let’s break down the calculation process:
1. Convert relative humidity from percentage to decimal form (divide by 100)
2. Calculate the intermediate value α(T,RH) using the formula above
3. Plug α(T,RH) into the main dew point formula
4. The result will be the dew point temperature in °C
## Example Calculation
For air at 25°C with 60% relative humidity:
1. RH = 60/100 = 0.6
2. α(25,0.6) = (17.27 × 25)/(237.7 + 25) + ln(0.6) ≈ 1.646 + (-0.511) ≈ 1.135
3. Td = (237.7 × 1.135)/(17.27 – 1.135) ≈ 269.8/16.135 ≈ 16.72°C
## Alternative Methods
While the Magnus formula is widely used, there are other approaches:
1. Psychrometric charts – graphical method using temperature and humidity
2. Online calculators – quick and convenient for non-technical users
3. Dew point meters – direct measurement instruments
## Practical Applications
Understanding dew point calculations is valuable for:
– Weather forecasting and analysis
– Preventing condensation in buildings
– Industrial processes requiring precise humidity control
– Agricultural planning and crop management
– Comfort assessment in indoor environments
## Limitations and Considerations
While the Magnus formula provides good estimates, remember:
– It works best for temperatures between 0°C and 60°C
– Accuracy decreases at extreme humidity levels
– Atmospheric pressure variations can affect results
– Different coefficients may be used for specialized applications
## Conclusion
Calculating dew point is an essential skill for many professionals and enthusiasts. By understanding the relationship between temperature and humidity, you can better predict condensation, assess comfort levels, and make informed decisions about environmental conditions. Whether you use the Magnus formula, charts, or digital tools, knowing how to determine dew point provides valuable insights into atmospheric conditions.
Keyword: how is dew point calculated